What is Tooth Whitening Gel?
Tooth whitening gel is a cosmetic dental product designed to lighten the shade of your teeth. It typically comes in the form of a gel that contains bleaching agents, most commonly hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. These agents work by penetrating the enamel and dentin of the teeth, breaking down stain molecules and resulting in a brighter, whiter smile. The gel is applied directly to the teeth, either at home using trays or strips, or in a professional setting by a dentist. The strength of the gel and the method of application can vary, impacting both the effectiveness and the potential side effects. Understanding the composition and intended use of whitening gels is crucial for assessing their safety and suitability for individual users. Proper usage and adherence to instructions are key to achieving desired results while minimizing risks.
How Does Tooth Whitening Gel Work?
The mechanism behind tooth whitening gel involves a chemical reaction that targets stain molecules within the tooth structure. The active ingredients, hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, release oxygen molecules. These oxygen molecules penetrate the porous enamel and dentin, breaking down the bonds of stain molecules. This process effectively decolorizes the stain molecules, making them less visible and resulting in a lighter tooth shade. The process is gradual, with noticeable changes typically appearing over a period of days or weeks, depending on the concentration of the whitening agent and the frequency of application. The effectiveness can be influenced by the type of stains, the individual’s oral health, and the specific product used. Regular use, as directed, is necessary to achieve and maintain the desired level of whitening.
Key Ingredients & Their Roles in Tooth Whitening Gel

The primary active ingredients in tooth whitening gel are hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is a stronger bleaching agent and is often used in professional treatments. Carbamide peroxide breaks down into hydrogen peroxide and urea, providing a slower release of the bleaching agent, making it suitable for at-home use. Other ingredients may include water, thickeners, flavoring agents, and desensitizing agents. Thickeners ensure the gel adheres to the teeth, while flavoring agents improve the taste. Desensitizing agents, such as potassium nitrate, help to minimize sensitivity. The concentration of the active ingredient significantly impacts the gel’s efficacy and potential side effects. The overall formulation of the gel is designed to maximize whitening effectiveness while minimizing potential adverse effects, such as sensitivity or gum irritation. Always review the ingredient list to ensure the product is safe for your specific needs and sensitivities.
Hydrogen Peroxide & Carbamide Peroxide in Whitening Gels
Hydrogen peroxide is a potent oxidizing agent directly responsible for the bleaching effect. It rapidly releases oxygen molecules, which break down the stain molecules. Its concentration can range from lower percentages in over-the-counter products to higher concentrations used in professional settings, offering quicker and more pronounced results. Carbamide peroxide, on the other hand, is a more stable compound that breaks down into hydrogen peroxide over time. This slower release makes it gentler and more suitable for extended use. The concentration of carbamide peroxide also affects its bleaching power. Choosing between hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide depends on individual needs, sensitivity levels, and the recommendation of a dental professional. Both compounds are effective, but the choice should be based on a balance between desired results and potential side effects.
Fact 1 Tooth Whitening Gel Can Cause Sensitivity
One of the most common side effects of tooth whitening gel is tooth sensitivity. This occurs because the bleaching agents can temporarily open the pores in the enamel, allowing the whitening agents to reach the nerves within the teeth. This can result in a sharp, shooting pain when consuming hot or cold foods and beverages, or even when breathing in cold air. The degree of sensitivity varies from person to person and is often related to the concentration of the whitening agent and the duration of treatment. Sensitivity is usually temporary and subsides after the whitening treatment is completed or when the frequency of use is reduced. Taking precautions, such as using desensitizing toothpaste, can help mitigate this discomfort.
Understanding Tooth Sensitivity After Whitening

Tooth sensitivity after whitening is a common but temporary side effect. It arises due to the permeability of the enamel, which allows the whitening agents to penetrate the dentin and stimulate the nerves. Individuals with pre-existing sensitivity, thin enamel, or receding gums are more prone to experiencing this discomfort. The intensity of sensitivity can range from mild twinges to severe pain. Typically, sensitivity peaks during the treatment period and gradually decreases after stopping or reducing the frequency of use. Understanding the causes and duration of sensitivity can help manage it more effectively. If the sensitivity becomes too severe, consulting a dentist is advisable to assess the situation and explore alternative solutions.
Managing Sensitivity with Desensitizing Products
To manage tooth sensitivity, various desensitizing products can be used. Toothpastes containing potassium nitrate are a popular choice, as they help to block the nerve signals that cause pain. These toothpastes should be used for a few weeks before, during, and after whitening treatment to build up their protective effect. Fluoride treatments, available from your dentist or in some toothpastes, can also strengthen the enamel, making it less permeable. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can provide temporary relief from pain. Avoiding highly acidic foods and drinks can help reduce sensitivity. If the sensitivity is severe or persists, consult your dentist for professional advice and potential treatments, such as fluoride varnish or prescription-strength desensitizing agents.
Fact 2 Whitening Gels May Irritate Gums
Another potential side effect of tooth whitening gel is gum irritation. This occurs when the bleaching agent comes into contact with the soft tissues of the gums, causing inflammation and discomfort. The irritation can manifest as redness, swelling, and tenderness. Improper application, such as using too much gel or using trays that don’t fit well, can increase the risk of gum irritation. Overuse of whitening products can also contribute to this problem. It’s essential to follow the product instructions carefully and ensure the gel is applied only to the teeth, avoiding any contact with the gums. If gum irritation occurs, it’s important to stop using the product and consult a dentist if the symptoms are severe or persistent.
Identifying Gum Irritation Symptoms
Identifying gum irritation symptoms early can prevent more severe complications. Common signs include redness, swelling, and tenderness of the gums, often along the gum line. You might also experience a burning sensation or increased sensitivity in the affected areas. The gums may appear irritated or inflamed. Sometimes, you may notice small white spots on the gums, which are areas where the bleaching agent has come into direct contact. If any of these symptoms appear, it’s crucial to stop using the whitening gel immediately. Consulting a dentist is advisable, especially if the irritation is severe or persists, as they can assess the damage and recommend appropriate treatment.
Preventing Gum Irritation During Whitening
Preventing gum irritation involves careful application and adherence to product instructions. Always use the correct amount of gel and avoid overfilling trays or applying the gel directly to the gums. Ensure the whitening trays fit properly, covering only the teeth and not the gums. Consider using a desensitizing gel or a barrier product to protect the gums. Avoid brushing your teeth immediately before whitening, as this can irritate the gums. If irritation occurs, discontinue use, rinse your mouth with water, and consult your dentist. Proper oral hygiene, including gentle brushing and flossing, can also help prevent gum irritation and promote overall oral health.
Fact 3 Effectiveness Varies by Stain Type
The effectiveness of tooth whitening gel varies depending on the type of stains present on your teeth. Extrinsic stains, which are on the surface of the enamel, are generally easier to remove. These stains are often caused by foods and drinks like coffee, tea, red wine, and certain spices. Intrinsic stains, which are embedded within the tooth structure, can be more challenging to address. These may be due to aging, genetics, medications, or excessive fluoride exposure. Whitening gels are typically more effective on extrinsic stains, while intrinsic stains may require more extensive or professional treatments. Understanding the type of stains can help you manage expectations and choose the most appropriate whitening method. Consulting with a dentist can help determine the origin and severity of stains and recommend the most suitable whitening approach.
External vs Internal Tooth Stains

External stains, or extrinsic stains, are on the surface of the enamel. They are typically caused by dietary habits, such as consuming dark-colored foods and beverages (coffee, tea, red wine, berries, and curries) or from smoking. External stains are generally easier to remove with whitening gels and can often be addressed with over-the-counter products. Internal stains, or intrinsic stains, are those within the structure of the tooth. These can be caused by factors like aging, genetics, certain medications (such as tetracycline), or excessive fluoride intake during tooth development. Intrinsic stains may require stronger whitening treatments, professional dental procedures, or other solutions to achieve the desired results. Recognizing the distinction between these two types is essential for setting realistic expectations and choosing the proper whitening approach.
How Whitening Gels Target Different Stains
Whitening gels use different mechanisms to target external and internal stains. For external stains, the peroxide agents in the gel break down the stain molecules on the tooth’s surface, effectively removing them. The process is relatively quick, and results can be noticeable within days or weeks. For internal stains, the peroxide agents penetrate the enamel and dentin, breaking down the stain molecules from within. This process can take longer and may require stronger concentrations of the whitening agent or multiple treatments. The effectiveness of the gel also depends on factors like the concentration of the active ingredient, the duration of application, and the individual’s oral health. Some stains may not respond well to whitening gels and might require alternative treatments, such as veneers or bonding.
Fact 4 Safety Depends on Gel Strength & Usage
The safety of tooth whitening gel is significantly influenced by its strength and how it’s used. Over-the-counter products typically contain lower concentrations of hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, making them generally safer for at-home use. However, it’s still crucial to follow the instructions carefully and avoid overuse. Professional whitening treatments performed by a dentist often use higher concentrations, providing quicker and more dramatic results. The dentist can carefully monitor the procedure and take steps to minimize risks, such as protecting the gums and adjusting the gel’s application time. Improper use, such as using a gel with a higher concentration than recommended or not following the directions, can increase the likelihood of side effects like sensitivity and gum irritation. Always choose products from reputable brands and consult your dentist for personalized advice.
Professional vs Over-the-Counter Gels
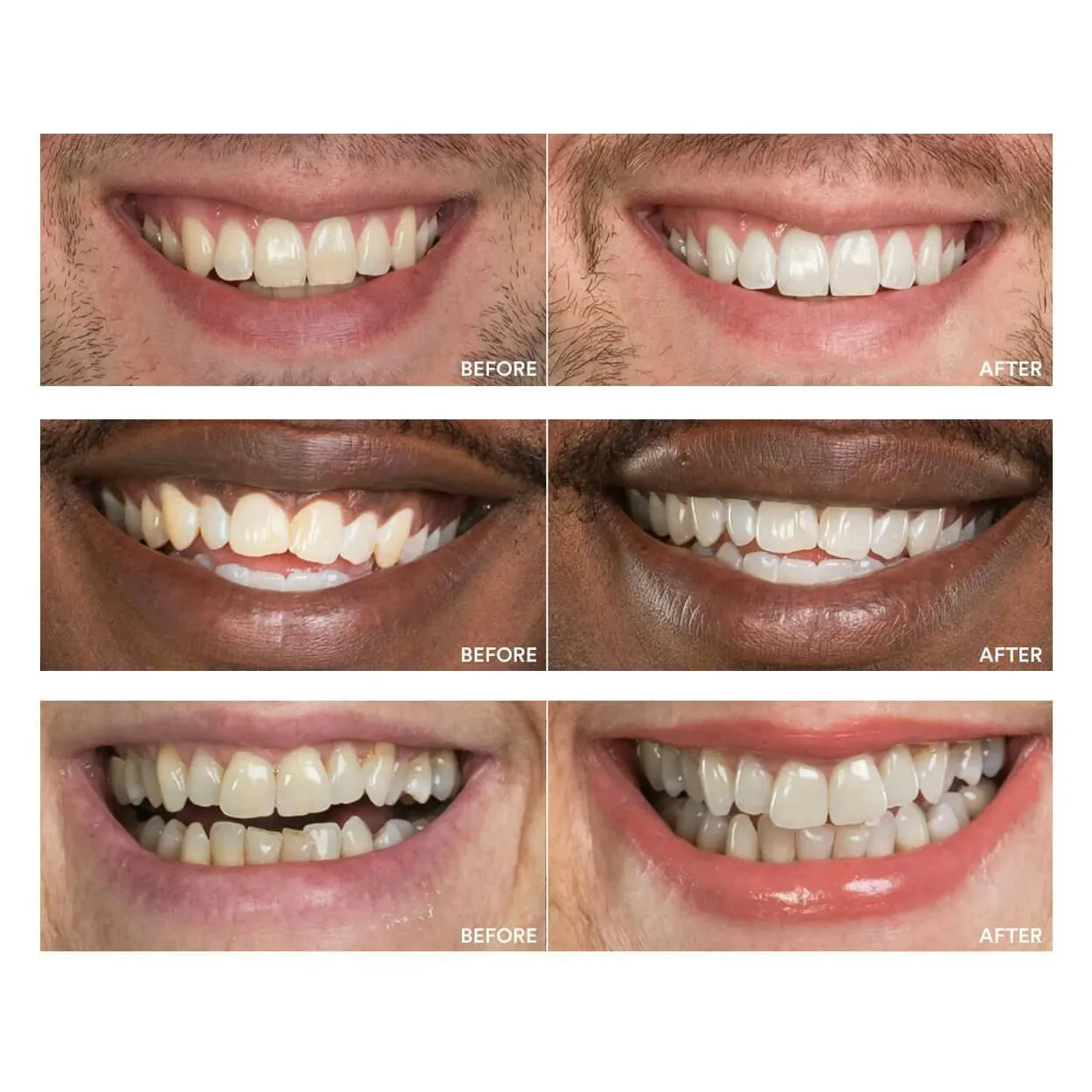
Professional tooth whitening gels, available from dentists, usually have higher concentrations of bleaching agents, such as hydrogen peroxide. This can result in faster and more pronounced whitening effects. A dentist supervises the procedure, ensuring the gums and soft tissues are protected. This professional approach can minimize risks, like gum irritation and sensitivity, and provides a more controlled whitening experience. Over-the-counter (OTC) gels contain lower concentrations of the active ingredients and are designed for at-home use. They are generally considered safer but may provide less dramatic results. Always follow the instructions carefully when using OTC products, and consult your dentist for personalized recommendations. Both options have potential side effects, so understanding the differences can help you make an informed choice.
Following Instructions for Safe Whitening
Adhering to the product’s instructions is paramount for ensuring the safety of tooth whitening gel. Always read and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines on the correct amount of gel to use, the duration of each application, and the frequency of use. Avoid exceeding the recommended usage, as this can increase the risk of sensitivity and gum irritation. Ensure proper tray fit to avoid the gel coming into contact with your gums. If using trays, make sure they are clean and dry before applying the gel. Be cautious when using any additional products, such as whitening toothpaste or mouthwashes, as they might interact with the gel. If you experience any adverse effects, such as significant sensitivity or gum irritation, stop using the product and consult your dentist. By following the instructions, you can maximize the effectiveness of the whitening treatment while minimizing potential risks.
Fact 5 Potential Long-Term Effects & Research
While tooth whitening gel is generally considered safe when used correctly, it’s essential to be aware of potential long-term effects. Research on the long-term impacts is ongoing, but some studies suggest that frequent and prolonged use might lead to changes in the tooth enamel’s structure, making teeth more susceptible to staining or erosion over time. Excessive use might also increase the risk of tooth sensitivity and gum irritation. However, these effects are more likely to occur with misuse or overuse of whitening products rather than with following recommended guidelines. Regular dental checkups and discussions with your dentist are crucial for monitoring the health of your teeth and addressing any potential concerns.
Ongoing Studies on Tooth Whitening Safety

The safety of tooth whitening is a subject of ongoing research, with scientists continuously examining the long-term effects of different whitening agents and methods. Many studies focus on the impact of whitening on tooth enamel, dentin, and the overall oral health. Researchers are evaluating the effects of different concentrations of hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide, the duration of the treatment, and the frequency of use. These studies aim to determine the safest and most effective ways to whiten teeth while minimizing risks. The findings from these studies help refine recommendations for usage and formulation and provide valuable insights into potential long-term effects. Staying informed about current research findings is crucial for making informed decisions about teeth whitening.
Minimizing Risks & Promoting Oral Health
To minimize risks and promote overall oral health during teeth whitening, there are several steps you can take. Always follow the product instructions carefully and avoid overuse. Use desensitizing toothpaste or other products to manage any sensitivity. Ensure the whitening trays fit properly to prevent gum irritation. Regular dental checkups are crucial for monitoring the health of your teeth and gums. Discuss your whitening plans with your dentist before starting any treatment, as they can provide personalized recommendations. Maintain good oral hygiene habits, including brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash. Consider limiting your consumption of foods and drinks that can stain your teeth. Combining safe whitening practices with good oral hygiene habits ensures a brighter, healthier smile.
Conclusion
Tooth whitening gel can be a safe and effective way to brighten your smile when used correctly. Understanding the key ingredients, how it works, and potential side effects is essential. Following instructions, choosing the right product for your needs, and consulting with a dental professional can minimize risks and ensure the best results. Sensitivity and gum irritation are common side effects, but they are often temporary and manageable. Ongoing research continues to evaluate the long-term effects of whitening, underscoring the importance of informed decision-making and good oral hygiene. By taking these steps, you can confidently achieve a whiter, healthier smile.